What is an Overhead Crane? 5 Factors to consider when choosing a crane
WHAT IS AN OVERHEAD CRANE?
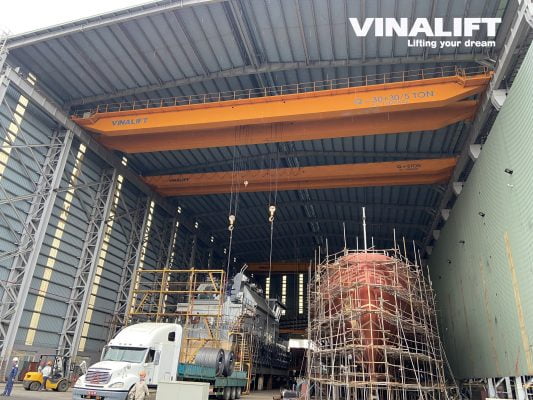
An overhead crane is a significant concept in the industrial and construction sectors. Known by various names such as overhead cranes, hoist cranes, electric cranes, or manual cranes, they facilitate production, construction, and transportation processes. So, what is an overhead crane? This article will help you understand overhead cranes’ structure, operation, and common applications.

What is an Overhead Crane?
According to Wikipedia. an overhead crane is a type of material handling equipment used to lift, lower, and move loads within a workshop or factory. This equipment is known for its convenience and high productivity in loading and unloading goods, with lifting capacities ranging from 1 to 500 tons. Electric motors primarily operate overhead cranes, making them widely used in industrial manufacturing plants and industries that require handling heavy loads.
An overhead crane has two main movements: the horizontal movement of the crane trolley along the workshop’s height and the vertical movement of the hoist (hook) to lift and lower the load. The crane trolley, which carries the hoist, can be a single girder beam, double girder beam, box girder, or suspension girder. The hoist is the part responsible for lifting and lowering the load and can be a chain hoist or wire rope hoist.
Types of Overhead Cranes
• By Functionality: There are two main types—general-purpose overhead cranes and specialized overhead cranes. General-purpose overhead cranes are typically used for loading, unloading, moving, installing, and repairing machinery. Specialized overhead cranes are used in specific industries such as metallurgy, hydroelectric power, explosives, etc. Specialized cranes come with unique attachments and heavy-duty working modes.
• By Drive Mechanism: Two types are manually operated overhead cranes and electrically operated overhead cranes. Manually operated overhead cranes use human-powered mechanisms like hand-cranked winches or hand-operated chain hoists. Electrically operated overhead cranes use electric motors or electric wire rope hoists.
• By Beam Structure: There are three types—single girder overhead crane, double girder overhead crane, and suspension overhead crane. Single girder overhead cranes have one main girder for suspending the hoist, usually an I-beam or box beam. Double girder overhead cranes have two main girders for hoist suspension, typically box girders or truss girders. Suspension overhead cranes do not have a main girder and instead have auxiliary beams suspended on overhead rails in the workshop.
• By Usage Scope: There are various types based on lifting purposes, such as port cranes, metallurgical cranes, hydroelectric cranes, explosive handling cranes, etc. These types often come with special attachments like grab buckets, electromagnets, etc.
Main Applications of Overhead Cranes for Factories:
- Mechanical manufacturing plants
- Processing plants
- Shipbuilding yards, hydroelectric, and thermal power plants
- Precast concrete pile plants
- Steel plants
- Warehouses

Factors to Consider When Choosing an Overhead Crane:
The choice of an overhead crane depends on several key factors, including:
Lifting Capacity: For loads under 25 tons, a single girder overhead crane is suitable.
Span: Single-girder overhead cranes are advantageous for spans under 25m, while double-girder overhead cranes are preferable for larger spans.
Equipment Layout:
- Lift Height: Single girder overhead cranes may limit lift height. For optimal lift height requirements, double girder overhead cranes are preferable.
- Distance from rail to beam end: In cases of limited space, a single girder overhead crane may be chosen. If ample space is available, a double girder overhead crane can be selected.
- Working range of the hook: Double girder overhead cranes offer an optimal working range for the hook compared to single girder overhead cranes.
Equipment Operation and Working Speeds:
- Light to medium-duty operation: Single girder overhead crane
- Heavy-duty operation, high working speeds, and demanding environments: Double girder overhead crane
Overhead Crane Operating Modes:
According to Vietnamese lifting equipment standards (TCVN 4244-2005) and FEM1.001, overhead cranes are categorized into eight operating modes from A1 to A8. These modes vary based on the type and purpose of the crane. The classification is as follows:
| No. | Type and Function of Overhead Crane | Crane Group |
| 1 | Manually operated overhead crane | A1, A2,A3 |
| 2 | Overhead crane for construction and installation | A4,A5 |
| 3 | Overhead crane for disassembly, assembly, and repair of power plants, in machine repair shops | A4 |
| 4 | Overhead crane for transporting materials in warehouses | A5 |
| 5 | Overhead crane in workshop | A5 |
| 6 | Overhead crane for use in demolition plants, landfills | A6,A7,A8 |
| 7 | Overhead crane for use in mines | A8 |
| 8 | Overhead crane for unloading castings, opening furnace bottoms, and charging raw materials for metallurgical furnace | A8 |
| 9 | Overhead crane for use in steel forging shop | A6,A7,A8 |
| 10 | Overhead crane for loading and unloading goods, transporting containers in port | A6,A7,A8 |
| 11 | Overhead crane in port | A6,A7,A8 |
| 12 | Overhead crane in shipyard | A5 |
| 13 | Overhead crane for construction | A4 |
| 14 | Overhead crane for railways | A4 |
Group 1: Light-duty overhead cranes, infrequent use: A3, A4
Group 2: Medium-duty overhead cranes: A5
Group 3: Heavy-duty overhead cranes: A6
Group 4: Very heavy-duty, continuous operation overhead cranes: A7, A8
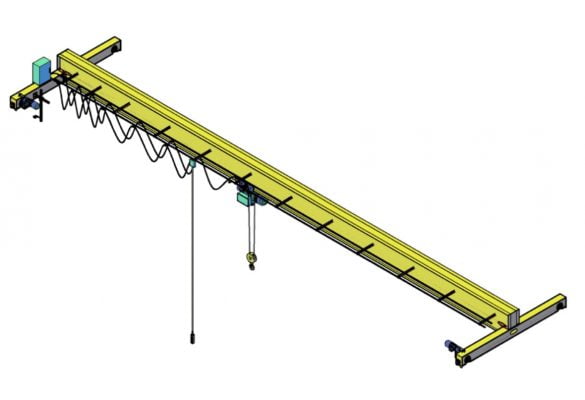
Structure of Single Girder Overhead Crane
=>>> READ MORE: SINGLE-GIRDER OVERHEAD CRANE
A single girder overhead crane consists of:
- Main girder: Box or I-beam type, 01 girder
- End beam (end girder): Combination type, 02 end girders
- Moving wheels: Made of S45C, 42CrMnO4, heat-treated 38~42HRC, using self-aligning bearings
- Hoist, electric winch
- Crane travel motor
- Control system: Inverter, contactor, automatic switch
- Deep groove cable
- Remote control or pendant control box
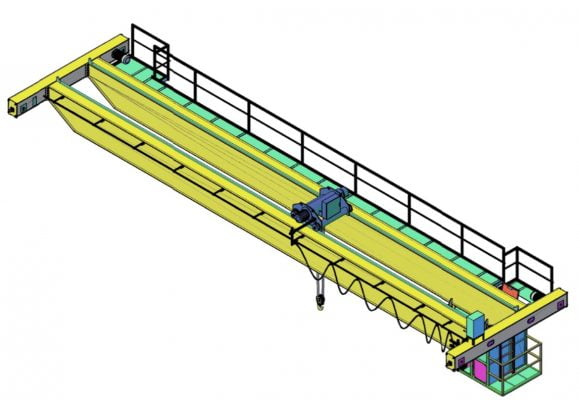
Structure of Double Girder Overhead Crane
=>>> READ MORE: DOUBLE-GIRDER OVERHEAD CRANE
A double girder overhead crane consists of:
- Main girder: Box girder type, 02 girders
- End beam (end girder): Combination type, 02 end girders
- Operator platform, railing
- Moving wheels: Made of S45C, 42CrMnO4, heat-treated 38~42HRC, using self-aligning bearings
- Hoist, electric winch
- Crane travel motor
- Control system: Inverter, contactor, automatic switch
- Deep groove cable
- Remote control or pendant control box
Control Options for Overhead Cranes:
Overhead cranes have various control options:
- Cabin control mounted on the main girder
- Remote control
- Hand-held pendant control box for moving along the girder or moving independently of the girder.
Each control option has its advantages and disadvantages. However, remote control is the most cost-effective option.
Safety Features:
Safety is crucial in the use of overhead cranes for plant operations to prevent accidents and ensure a secure working environment. To ensure safe crane operation, the overhead crane must have the following minimum safety warning devices:
- Overload warning
- Limitation of lifting range: Two levels – level one control cutoff, level two dynamic cutoff
- Limitation of trolley travel range: Two levels – level one control cutoff and high speed, level two dynamic cutoff or slow speed.
- Limitation of crane travel range: Two levels – level one control cutoff and high speed, level two dynamic cutoff or slow speed.
- Bumpers at the end of travel distance: Rubber type with steel stops.
- Horn, warning lights during crane movement
- Starting bell.
- Load display board
- Load sway control (Anti-sway).
- Anti-collision device for cables
- Cable guidance
Notes on Usage and Maintenance
Like any other equipment, overhead cranes require regular maintenance to ensure safety and continuous operation, prolonging the crane’s lifespan.
Key considerations include:
- Check the condition of gearbox oil, grease bearings, and wire rope lubrication.
- Inspect the condition of wire ropes for timely replacement and removal.
- Examine the condition of contactors, automatic switches, fuses, and circuit breakers.
- Verify the condition of travel paths.
- Check the condition of overload indicators.
Maintenance Schedule:
Overhead crane maintenance is categorized into three types:
- Daily Maintenance: Before starting the work shift, operators should perform a preliminary check of the equipment and obstacles on the crane and rail.
- Monthly Maintenance: Check the equipment condition and replenish lubrication.
- Annual Scheduled Maintenance: Detailed inspection of each component, providing a comprehensive report for replacement, supplementation, or user warnings.

